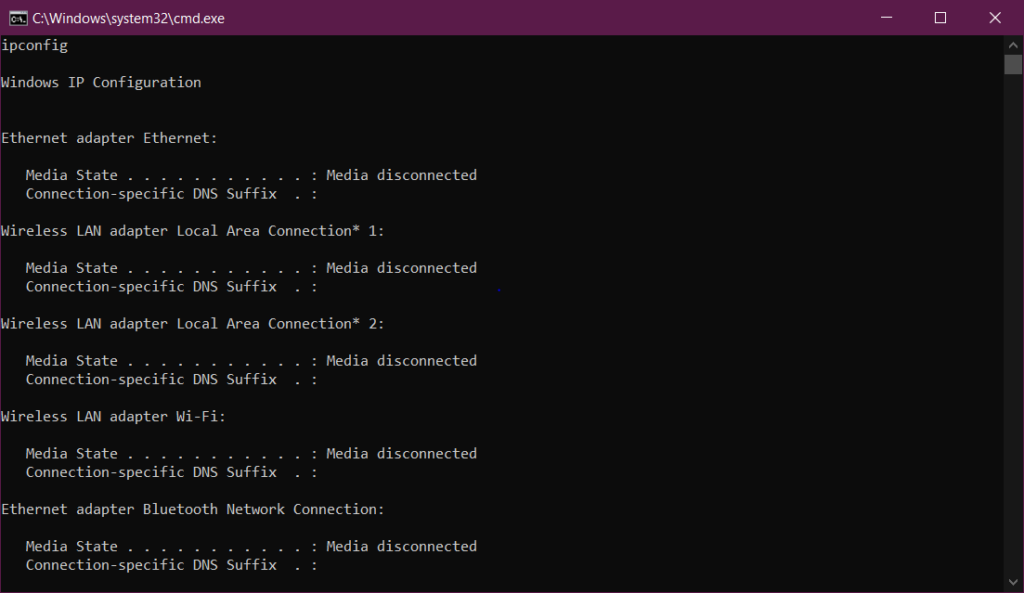
To view details about your network setup and update your DHCP and DNS settings, use the ipconfig command. via default, your IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway are displayed via the ipconfig command. However, you can get a lot more information from it if you set the right parameters. Here are instructions for using it.
- To run the command, open the Command prompt on Windows PC or Terminal on Mac.
- Type ipconfig and press Enter. This will display information about each network adapter on your computer. including any VPN connection that you might have.

- Type ipconfig /all and press Enter. This will show all the information about your network adapter:
- Physical Address: This is the MAC address of your network adapter.
- DHCP Enabled: Indicates if the network connection is using DHCP or Static IP Address
- IPv4 Address: The IP Address of your computer
- Default Gateway: The router to which your computer is connected
- DHCP Server: Router/server that hands out IP Addresses in your network
- DNS Servers: Servers used to translate domain names to IP Addresses
- Link-Local IPv6 Address: IPv6 address of your computer (often not used)
- Lease Obtained: Date-time when your computer received the IP Address

- When you have DHCP enabled on your network card, you can request a new IP Address from the DHCP server. To do this:
- Type ipconfig /release adapter_name
- Then type ipconfig /renew adapter_name
- Your computer keeps a local cache of DNS records of websites it has visited. This cache is used to convert domain names into IP Addresses. If you want to see the content of the DNS cache on your computer just type ipconfig /displayDNS.